How To Monitor Multi-System Business Processes
Organizations use processes to manage their business. How each process gets implemented falls into four main categories.
- Paper-based
- Email + Spreadsheet
- Multiple Systems
- BPM Software
Organizations have invested a lot of time and money in processes that fall into category 3. Bringing all those processes into a BPMS is not an easy or quick job. I have seen a single process that goes through 20+ systems from start to end.
Let's take an example of order fulfillment, a fairly common process. The diagram below shows lifecycle of an order as it moves through various systems. Most of the times you will find core business of an organization distributed into multiple systems in a similar manner. Work, of course, gets done, but at any given time you cannot find exactly what is the current status of the process. And to generate even simple reports, data first needs to be consolidated from all the systems manually or through some sort of batch job.

So, how do you monitor a process that resides in multiple systems and ensures that it is running optimally considering it does not provide a single view. You build a shadow process.
The idea of shadow process is simple; you design the end to end process with all major milestones without actually implementing all the functionality in a BPMS.
Implementation Steps
Here are high-level steps for implementing a monitoring system using shadow processes.
- Define process with major milestones
- Level of milestone granularity is directly proportional to effort required
- Use milestones that make sense for reporting

- Find a common id that will allow you to uniquely identify an instance of the process in all systems
- Build services that either receives events from external systems or fetch data from external systems
- Build services that advance the process instance based on event data

- Log key event data e.g. instance id, business data, start time and end time etc. These can then be used by any reporting tool to generate meaningful insights

Compared to implementing all the processes in a BPMS, this type of monitoring solutions is much quicker to implement, provide end to end process view and helpful insights for future optimization.
Why Digital Transformation Can't Proceed Without Operational Process Transformation
MWD Advisors’ Neil Ward-Dutton reently did a webinar explaining how digital transformation can't proceed without process digitization.
As usual, he is absolutely correct! Organizations going through digital transformation journey focus more on transforming customer experience and business model. Both of these areas are visible to the customer hence considered more important than operational processes.
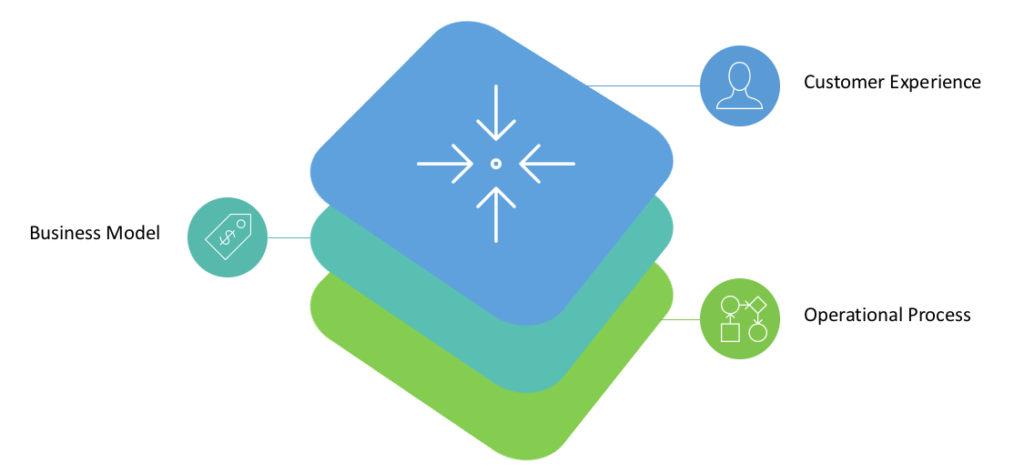
A great looking website, mobile app or a digital product is required, they will (likely) result in great customer conversion rates, but in all cases, they will trigger or interact with some internal process. An organization will be able to acquire new customers of course, but customer retention will heavily depend on how good or bad their internal processes are.
Internal processes should not be visible to the customer. A bad internal process will be visible to the customer, it will not only annoy the customer but frustrate workers as well. A good process, on the other hand, will be invisible, which should be the goal. The customer experience should be so seamless that a customer should not need to know an organization's internal processes.
There are three building blocks of operational process transformation:
- Process Digitization
- Worker Engagement
- Performance Management
Organizations can focus on each of these building blocks to transform their operational processes, which in turn advances them in their digital transformation journey.
Read more about operational process transformation.
What is Digital Transformation?
Digital transformation is the latest buzz word being used by all the consulting companies and organizations, but what is it? One of the more comprehensive definitions that I have found is from i-scoop.eu.
Digital transformation is the profound and accelerating transformation of business activities, processes, competencies and models to fully leverage the changes and opportunities of digital technologies and their impact across society in a strategic and prioritized way.
Source: i-scoop.eu
Another simpler definition of digital transformation can be found from Wikipedia.
Digital transformation is the changes associated with the application of digital technology in all aspects of human society.
Source: Wikipedia
In my opinion, digital transformation is not just about technology. The digital part, of course, can only be achieved using technology, but transformation requires vision, strong leadership and strategy.
A research report from MIT Sloan Management Review identifies three key areas that organizations can focus on for digital transformation.

For each area, the report also provides three elements that are changing.
- Customer Experience
- Customer Understanding
- Top-line Growth
- Customer Touch Points
- Operational Process
- Process Digitization
- Worker Enablement
- Performance Management
- Business Model
- Digitally Modified Business
- New Digital Businesses
- Digital Globalization
These elements provide a good starting point for organizations looking to digitally transform. Of course focusing on all of them at once might be overwhelming, so each organization will need to prioritize what elements to focus on based on their goals.
How To Improve Worker Engagement Using Process Gamification
Note: This article was originally published on my previous blog ProcessRamblings.com.
Gamification is the use of game thinking and game mechanics in non-game contexts to engage users in solving problems and increase users’ self-contributions. If implemented in the right manner, gamification can be a great tool for sustained engagement. Laura Lilyquist of Badgeville defines sustained engagement as
“the kind of engagement that naturally occurs over the long term and becomes permanently ingrained into the culture”.
In this article, we are going to discuss what game elements can be used in business processes to improve worker engagement.
Points System
As humans, we seek recognition and acknowledgment for a job well done or for going the extra mile to help the organization. Games use a points-based system and recognize players’ performance in various different ways such as unlocking new levels, giving additional “goodies” and awarding achievement badges.
A similar concept of points-based system can be used to reward process workers as well. Following list provides various activities that can be used to award points.
Challenges – task completion cycle times can be used as challenges for users e.g. different points can be awarded based on the time taken to complete a task.
- Task Completion Time < 1 Day = 3 Points
- Task Completion Time > 1 Day & < 2 Days = 2 Points
- Task Completion Time > 2 Days = 1 Points
Performance – points for initiating or completing a certain number of tasks over a specified period of time e.g. sales lead generation.
Feedback – this is an important one to measure and reward because this would normally lie outside of a workers job duties.
Share Improvement Ideas – providing process improvement feedback to process owner through the system.
Content Feedback – starting a discussion thread about a process feature or anything that could be useful for others working on the process.
Commenting/Answering Questions – participating in discussions by commenting or answering questions.
Reports & Filters – if there are ad-hoc reports, then sharing those reports and possible search criterion could be very beneficial for other users, increases collaboration and avoids reinvention of the wheel.
Rework – nobody likes rework, so just like games reduce points, there should be a negative impact on the user’s score for causing rework. Rework can be calculated based on process loopbacks, data hygiene and data accuracy etc.
Achievement Badges
 Points awarded to users become the basis for recognizing achievements. For instance, a user who consistently resolves 10 cases a day for a period of 30 days can be awarded the Case Guru badge. Badges are usually funny and quirky, something that people will enjoy and can feel proud of when displayed on their profiles.
Points awarded to users become the basis for recognizing achievements. For instance, a user who consistently resolves 10 cases a day for a period of 30 days can be awarded the Case Guru badge. Badges are usually funny and quirky, something that people will enjoy and can feel proud of when displayed on their profiles.
Similarly, points can also be used to assign relatively simpler tasks to newbie’s as compared to assigning difficult tasks to more experienced users. In games, this can be seen as transitioning from Newbie to more Advanced levels.
Leaderboards
 Leaderboards are perhaps the most popular gamification technique used in non-game contexts. Leaderboards are a motivational tool where users get to compare their scores or performance with peers.
Leaderboards are perhaps the most popular gamification technique used in non-game contexts. Leaderboards are a motivational tool where users get to compare their scores or performance with peers.
Leaderboards should use a similar scoring mechanism i.e. rank users working in similar process areas ensuring we compare apples to apples and not apples and not apples to oranges.
 Leaderboards bring out the competitive nature in humans and cause “shame” in losing. So, a recommended approach is to use team leaderboards as well, this encourages cooperation and creates a more collaborative environment.
Leaderboards bring out the competitive nature in humans and cause “shame” in losing. So, a recommended approach is to use team leaderboards as well, this encourages cooperation and creates a more collaborative environment.
Activity Streams
Live activity streams can be used to display user accomplishments to everyone as and when they happen. Accomplishments can include completion of a task, milestone or earn a badge. Unlike leaderboards which provide cumulative data, activity streams provide more visibility to individual achievements.
Goals
The concept of team games should be used i.e. all players on a team playing for the same goal. The goal should not be winning or obliterating the opponent, instead of in an organization focus should be on creating a more collaborative environment.
In games providing upfront goals such as how many points need to be scored, coins need to be collected or enemies need to be destroyed gives players a clear idea at each moment about what needs to be done in order to complete the level. Similarly, process works should have clear goals e.g. not working on easy cases, instead of working on the case with a higher dollar value and other organizational goals.
Progress
Process workers should continuously know their progress towards achieving their goals, this could be either displaying amount of dollars they have recovered for the organization or what stage are they in the process.
Helpful Hints
Complex and nicely designed games provide on-screen hints and guides which are extremely helpful for new players. Help, hints, and wizards should be included for process workers as well, these will definitely help reduce the training time for new users and of course existing users can always refer to them in case they are stuck for any reason.
Conclusion
 As mentioned in the beginning of this article, if implemented in the right manner gamification can significantly improve process worker’s engagement.
As mentioned in the beginning of this article, if implemented in the right manner gamification can significantly improve process worker’s engagement.
- Gamification should not be forced on the users because that is not any different from the current stick approach. Gamification also should not be a carrot approach i.e. expecting to get more work out of user’s just because they will be rewarded. It should be implemented with user’s consent, both carrot and stick approaches do not work in the longer term.
- Gamification should focus on individuals working to organization’s goals, it should not be used to shame individuals with lower points/score/performance.
- The rewards system should be appropriate according to the nature of job e.g. a sales person closing new leads in time should definitely be called a Sales Guru, but it should not replace their monetary compensation.
References
- 6 Critical Game Mechanics to Consider in Leaderboards (Part 1)
- Employee Engagement Drives Optimal Business Results
- Psychology of High Scores, Leaderboards, & Competition
- Gaming for Reality – Can BPM be Fun?
- Gamifying processes: seductive, but proceed with caution
- OpenClipArt.org
How To Empower Knowledge Workers Using Cognitive BPM
Note: This article was originally published on my previous blog ProcessRamblings.com.
Throughout the lifecycle of a business process knowledge workers are required to make decisions based on their domain knowledge.
IBM® Watson™ is an artificially intelligent computer system with the capability to answer any domain related questions in a natural language.
In this article, we are going to take a look at how different IBM® Watson™ services can be used within business processes to empower knowledge workers in making better decisions.

Personality Insights
Enables deeper understanding of people’s personality characteristics, needs, and values to help engage users on their own terms
Example: This service can be utilized in processes such as New Hire. It can be used to analyze various personality characteristics of a candidate. It analyzes the input text which in our example can be candidates profile, emails or any other communication. The output will be both in natural language and visual formats as shown in diagrams below. This output can help in deciding if the candidate is a good fit for the organization or not.


Concept Insights
Explores information based on the concepts behind your input, rather than limiting investigation to findings based on traditional text matching
Example: Processes such as Talent Acquisition that currently use keyword-based search can tremendously benefit from this service. The traditional keyword-based searches might not always return the desired results because if an exact match is not found the document and in our case, a resource profile will simply be ignored. The Concept Insights service, on the other hand, looks for conceptually related items i.e. even if the input keywords do not exactly match, this service will try to find content that is related to the same concept. In our example, a resource profile might not match the exact keywords, but it will still show up in the search results even if the resource profile has different keywords or they have worked in a related area.

Tradeoff Analytics
Helps users make better choices to best meet multiple conflicting goals, combining smart visualization and recommendations for tradeoff exploration
Examples: Tradeoffs are an integral part of the decision-making process. This service can help recommend the best possible case that meets organizational goals.
This service can be utilized in the supply chain processes for selecting best possible suppliers, sourcing low-cost parts etc. The service provides a very visual way of performing this analysis as shown in the diagram below.

Another great utility is in the patient case management where this service can help decide the best treatment options and drugs for patients.

Similarly, this service can be used in financial asset management processes to make informed decisions about choosing the best assets for investment.
Language Identification / Machine Translation
Identifies the language in which text is written
Globalize on the fly. Translate text from one language to another
Example: These are two distinct services, one that identifies which language is the input text written in, while the second one translates it. For larger organizations that operate globally, this is an essential requirement. This service just makes the whole globalization process easy by automatically translating the text.
Question And Answer
Direct responses to user inquiries fueled by primary document sources
Example: This service provides answers to questions in a natural language thus making it a great source for getting additional domain-specific information. The answers that the service returns also include Watson’s confidence level as a percentage.
The service can be used in all types of processes such as in travel and hospitality processes for finding out visa and vaccination requirements of a country or in the healthcare industry for getting more information about a disease.

Conclusion
In addition to the IBM® Watson™ services mentioned above, there are quite a few other services that are currently available, such as:
- Concept Expansion
- Relationship Extraction
- Message Resonance
- Speech to Text
- Text to Speech
- Visual Recognition
- Visualization Rendering
All of these services are available on IBM® Cloud™, can be easily developed using Bluemix™ and consumed within any Business Process Management (BPM) or Case Management tool. For now, these can be used to support and empower knowledge workers in making decisions but in future, these can and will be used to automate the decision-making process.
References
- IBM® Watson™ Services Catalog – Used for service definitions
- Integrate IBM BPM with IBM Watson, Part 1 by Raj Mehra
- Integrate IBM BPM with IBM Watson, Part 2 by Raj Mehra
Disclaimer: IBM® Watson™, IBM® Cloud™ and Bluemix™ are trademarks or registered trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation.
Republished/Cited
- Article republished on BPTrends.com
How Process Mining Finds Hidden Business Processes
Note: This article was originally published on my previous blog ProcessRamblings.com.
In this article, we are going to discuss what type of gaps are left by existing process analysis techniques, what is process mining and what are the benefits of applying process mining techniques during analysis and how to apply these techniques.
Gaps In Process Analysis Techniques
First, let’s take a look at the cases in which existing process analysis techniques fail and result in process gaps.
The picture on right is taken from the process mining course that is offered by Eindhoven University of Technology. It gives insight into an important human behavior of
Shortcuts.
Shortcuts are very common in our daily lives. As the picture shows there might be a perfectly laid out path in front of us, but most of us will still create our own shortcut through the grass.
The same practices can be seen in our work lives. An organization can have very well defined processes, but workers still find a way to bypass them. These bypasses are usually the most commonly executed flows of the process (a.k.a. Process Highways), yet in most cases remain undocumented.
During process analysis, requirements are usually captured from the following sources:
- Workers/Performers
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOP)
- Process Documentation
- Industry Standards
All these sources provide information on the as-is process i.e. how it has been defined or how the process is supposed to flow. This does not necessarily reflect the reality and as a result, we find gaps between the defined process and the executed process.
Defined versus Executed Process
To further elaborate this gap, consider the example of a simple Expense Claims Process. The first process model shows what is the defined flow of an expense claim request. The assumption is, that 100% of claims after submission go for Manager’s approval. Manager approves or rejects them, and in the case of approval, they move to the Finance team’s queue for reimbursement.

In reality, workers do not follow the defined process. If we were to look at the historical data of the process, we might find that in reality only 30% of claims are sent for Manager’s approvals. 70% of claims are directly sent to Finance team for reimbursement.

We have established that people bypass defined processes and they create their own shortcuts, yet most of the process analysis techniques we use only look at the defined as-is processes and simply ignore these bypasses. So this results in gaps between the defined process and the executed process.
What is Process Mining?
In the expense claims process example what actually helped us in identifying the gap?
Data
This is exactly what process mining techniques do. They allow us to extract real process information from the data. These techniques identify all possible paths of the process from events log and answer following questions:
- How are the cases actually being executed?
- What is the most frequent path for every process model?
- How is the distribution of all cases over the different paths through the process?
- How many people are involved in a case?
All these questions, help us in extracting the process paths that are actually executed in the organization.
How To User Process Mining Tools?
There are a few process mining tools available on the market. One of them is ProM, which is a free tool developed by Eindhoven University of Technology in collaboration with a few other universities and vendors.
At a high-level the usage of ProM is simple.
Step 1 – Retrieve events log of the process that needs to be analyzed. Events log usually has following information that can help identify transactions uniquely and correlate them.
Case ID | Activity Name | Performer | Timestamp
Step 2 – Events log are converted into an XML format that is understood by ProM.
Step 3 – ProM mines the data and generates all possible process paths using the standard BPMN. The generated model includes detailed information including all possible process paths, participants and number of times each flow is executed etc.

Conclusion
In my opinion, process mining techniques can be extremely useful in various different scenarios, such as:
- Process analysts can use these techniques to verify process models i.e. to ensure that all possible process paths and participants have been captured. These techniques can also be very valuable at the analysis and optimization stages.
- As more and more organizations make Internet of Things (IoT) an integral part of their processes (see auto insurance industry, waste management industry), we will need to mine data generated from these IoT devices. This data will help in understanding how these IoT devices create their own process highways.
Currently, the tools available for process mining are mostly standalone and have a relatively higher learning curve, as a result, there might be some reluctance on their usage. Even if you are not planning to mine data using the tools, the techniques themselves can be used. You can use the events log data to manually run all possible scenarios to make sure that the process model can handle real life situations.
Business Process Management Software (BPMS) vendors do provide simulation features, but they only work on historical data generated by the BPMS. So BPMS vendors need to add process mining features in their offerings as well (either by building from scratch or acquiring and integrating the already available tools).
If you are more interested in learning about process mining techniques then visit the links provided in the references section.
References
- Process Mining: Data science in Action
- ProM 6 Tutorial
- Discovering, Analyzing and Enhancing BPMN Models Using ProM
- Fluxicon – Webinar introducing a commercial process mining tool based on ProM
How To Improve Business Processes Using Internet Of Things (IoT)
Note: This article was originally published on my previous blog ProcessRamblings.com.
In this article, we are going to look at how different industries are leveraging (or can leverage) internet of things (IoT) to improve their business processes. These improvements can increase efficiency, improve data accuracy and resource utilization and most importantly increase customer satisfaction.
Auto Insurance - Additional Discount Process
 Recently all major auto insurance companies have started offering their customers additional discounts based on their driving performance. The customers are required to install a tracking device for a specified amount of time, once installed the tracking device starts transmitting data to the insurance company. The insurance company captures and evaluates the data until the trial period ends.
Recently all major auto insurance companies have started offering their customers additional discounts based on their driving performance. The customers are required to install a tracking device for a specified amount of time, once installed the tracking device starts transmitting data to the insurance company. The insurance company captures and evaluates the data until the trial period ends.
Here is an overview of the additional auto insurance discount business process. This does not include all the steps, only main activities have been included to keep it simple.
- Customer applies for the trial
- Insurance company mails the device
- Customer installs the device
- Device transmit analytics
- Insurance company captures analytics
- Insurance company evaluate captured data
- At the end of trial period, the insurance company applies additional discount (percentage is based on customer’s driving performance)

By leveraging IoT data both the auto insurance companies and customers are reaping multiple benefits such as:
- Insurance companies get more accurate driving data of customers for future analytics.
- Insurance companies utilize the captured data to provide an appropriate percentage of additional discounts to good performing customers, which further increases customer loyalty.
- Rather than waiting for the trial period to end, customers get access to their driving performance and expected discounts information live.
- To get higher discounts, customers can use the violations data (such as rapid acceleration and rapid braking) to improve their driving habits as well.
Waste Management - Garbage Collection Process
 Recently cities like Barcelona have moved from the traditional process where a garbage truck would have to make a scheduled route and pick up garbage cans regardless of them being full or empty.
Recently cities like Barcelona have moved from the traditional process where a garbage truck would have to make a scheduled route and pick up garbage cans regardless of them being full or empty.
Here is an overview of the new garbage collection business process. This does not include all the steps, only main activities have been included to keep it simple.
- Set Threshold (garbage cans have embedded systems to communicate)
- Garbage Can Transmits Analytics
- Receive Analytics
- Evaluate Data (check if the threshold has exceeded or not?)
- Calculate Smarter Route & Schedule Garbage Pickup

By leveraging IoT data the waste management companies are reaping (can reap) multiple benefits such as:
This process resulted in poor utilization of the garbage trucks, higher fuel costs and of course causing air and noise pollution.
- Improved resource utilization – Using IoT, companies would know which garbage cans have exceeded the thresholds and need to be picked up. This data could be used to calculate smarter routes resulting in a reduced number of routes as compared to sending garbage trucks to all pre-defined routes.
- Lower costs – Smarter routes will also help in lower fuel and maintenance costs of the garbage trucks.
- Lower pollution – Another great advantage would be the reduction in air and noise pollution.
Those were just a few examples of how the internet of things (IoT) is being used to improve business processes. There are numerous other processes that can benefit from the internet of things (IoT). In conclusion, organizations should start thinking about IoT and how it can exponentially improve their efficiency and customer’s experience.
Republished/Cited
- Article republished on BPMLeader.com
Why Organizations Should Continuously Improve Business Processes
Note: This article was originally published on my previous blog ProcessRamblings.com.
Continuous improvement is one of the most talked about phrases in the world of BPM, yet it is the most ignored idea when it comes to implementation. Continuous improvement prefers smaller bangs over a big bang or quick wins over big wins.
Unfortunately in order to make a wider base of users happy, BPM CoE tends to go for the big bang or the big win approach by adding more and more requirements to the scope. A process implementation project that takes more than 4 to 6 months before it is made available to users, should be re-evaluated for scope. Such projects should be split into multiple smaller phases.
Advantages of Continuous Improvement
This phased approach of implementing bigger projects in smaller chunks has quite a few advantages:
- Process Familiarity: Not all users are familiar with the new process, user interface or the BPMS. So, a small set of requirements helps them get acquainted, relatively quicker, with the new process and environment that they will be working with.
- Feedback: During requirement gathering sessions all users are not involved, so the sooner the process gets into production and becomes available, the sooner all intended users will start using it. When users start sending valuable feedback (like missing requirements, difficult user interface, etc.), then those can be incorporated into future phases to improve the process.
- Monitor/Optimize: It is a huge plus to monitor a process that is being used by real users instead of simulations. It provides additional metrics and insight into the process, and helps identify areas of the process that can be further optimized.
- Funding Cuts: Even if funding cuts occur, which are quite common, a significant and tangible piece of the process will be available for users to use. If it has been implemented correctly, then there is a very good chance that the process users will rally for the funding.
Recommended Steps
Here are a few steps that can break a big project into several smaller – manageable – phases:
- Look for higher ROI (Return of Investment): One of the most important success factors is ROI, so choose activities that contribute most to the ROI of the process. This would include activities that reduce cost and cycle time, while increasing resource utilization.
- Prioritize: Properly prioritize activities, and select the ones with the highest impact for a sure win.
- Swivel Chair: Not all activities need to be automated on day 1. The ones that might be too complex, or take a lot of time and effort to implement, and may or may not contribute as much to the process, can be left for later phases. So, leave some swivel chair activities.
Summary
My recommendation would be to implement a process automation project in phases and go for quick win/smaller bang in the first phase. Quicker time to production will help in getting valuable feedback from users who actually do the job, which can then be used to improve the process in future phases along with remaining requirements.
Republished/Cited
- Article republished on BPMLeader.com
How To Improve Business Processes Using Process Analysis
Note: This article was originally published on my previous blog ProcessRamblings.com.
In my previous post, I talked about mapping customer journeys i.e. as an organization you should understand all the touch points where your customers interact with you, and the resulting processes.
So you understand all customer touch points, what now?
Most organizations unfortunately have not invested in understanding their as-is processes. Things are working, so there is a general lack of urgency. As a process analyst I get to hear following statements a lot.
Why should we spend time and money to model our processes?
If it ain’t broke don’t fix it!
My answer is rather simple.
Well, how do you know it ain’t broke?
Just because things are working does not mean they are working correctly or more importantly, working optimally. You cannot tell if it’s broke or not unless you can answer following questions:
- What is their role in the process?
- What is the impact of their activities on the process and how are they adding value?
- And most importantly, how are they doing compared to their competitors?
These are the answers you get from a detailed process analysis effort. In this article we are going to look at a few important reasons why process analysis is so important, and why every organization should invest in that effort.
Current State (AS-IS)
The first step is to model your current end-to-end processes (a.k.a. as-is). Regardless of what techniques you use, so many unknowns will come to light that you did not even know were happening or causing issues.
Process Hand-offs
Most processes run across departments. Within an organization you cannot work in departmental silos, yet each department is only familiar with their part in the process. Gaps, redundancies and incorrect expectations can be identified and eliminated when all stakeholders look at the complete process.
Common Language
Process analysis effort helps in eradicating all the homegrown process models that use notations only understandable to the teams that created them. Their meaning is lost in translation when someone from outside the team tries to understand them. Try searching for process models on the internet, and you will see plethora of notations that absolutely do not make sense.
Process Hierarchy
Creating hierarchies, helps model the process with correct level of details. It also helps communicate the right amount of information to different levels of management while talking about process improvement.
Enterprise Repository
Another advantage of this effort at organizational level is that it results in an enterprise repository that is shared and is accessible to anyone. You always have access to all the versions of a process and comments from users who worked on them. Majority of tools now also provide collaborations i.e. multiple users can work on same process model.
Industry Benchmarks
When processes are modeled and various performance indicators are captured, it helps in bench-marking against organizations internal standards and industry standards.
Enterprise Architecture
Mapping processes and all the systems they interact with creates links for Enterprise Architecture. This information is extremely helpful during change management, just a couple of clicks and you can see exactly what processes would be impacted by a system change and vice versa.
Future State (TO-BE)
Modeling of as-is processes is just the first step. Use the outputs from this activity to identify issues, bottlenecks, redundancies and gaps in the process. Look at opportunities to automate various unnecessary and time consuming manual handovers. This will help you come up with the future state where you would like to be and then continuously keep reevaluating (a.k.a. continuous improvement).
Conclusion
Processes are everywhere. Processes manage an organization’s business. So, it is important for organizations to invest in knowing their processes. An important first step is doing a process analysis to understand how is the business being run currently and what can be improved in future. In an organization's digital transformation journey, understanding of processes also contributes towards prioritizing what improvements need to be made that can improve customer experience.
Republished/Cited
- Article republished on BPMLeader.com